Product Description
Machining Capability
Our Gear, Pinion Shaft, Ring Gear Capabilities:
| Capabilities of Gears/ Splines | ||||||
| Item | Internal Gears and Internal Splines | External Gears and External Splines | ||||
| Milled | Shaped | Ground | Hobbed | Milled | Ground | |
| Max O.D. | 2500 mm | |||||
| Min I.D.(mm) | 30 | 320 | 20 | |||
| Max Face Width(mm) | 500 | 1480 | ||||
| Max DP | 1 | 0.5 | 1 | 0.5 | ||
| Max Module(mm) | 26 | 45 | 26 | 45 | ||
| DIN Class Level | DIN Class 8 | DIN Class 4 | DIN Class 8 | DIN Class 4 | ||
| Tooth Finish | Ra 3.2 | Ra 0.6 | Ra 3.2 | Ra 0.6 | ||
| Max Helix Angle | ±22.5° | ±45° | ||||
Our Main Product Range
1. Spur Gear
2. Planetary Gear
3. Metal Gears
4. Gear Wheel
5. Ring Gear
6. Gear Shaft
7. Helical Gear
8. Pinion Shaft
9. Spline Shaft
Company Profile
1. 21 years experience in high quality gear, gear shaft’s production, sales and R&D.
2. Our Gear, Gear Shaft are certificated by ISO9001: 2008 and ISO14001: 2004.
3. CHINAMFG has more than 50 patents in high quality Gear, Gear Shaft manufacturing.
4. CHINAMFG products are exported to America, Europe.
5. Experience in cooperate with many Fortune 500 Companies
Our Advantages
1) In-house capability: OEM service as per customers’ requests, with in-house tooling design & fabricating
2) Professional engineering capability: On product design, optimization and performance analysis
3) Manufacturing capability range: DIN 3960 class 8 to 4, ISO 1328 class 8 to 4, AGMA 2000 class 10-15, JIS 1702-1703 class 0 to 2, etc.
4) Packing: Tailor-made packaging method according to customer’s requirement
5) Just-in-time delivery capability
FAQ
1. Q: Can you make as per custom drawing?
A: Yes, we can do that.
2. Q: If I don’t have drawing, what can you do for me?
A: If you don’t have drawing, but have the sample part, you may send us. We will check if we can make it or not.
3. Q: How do you make sure the quality of your products?
A: We will do a series of inspections, such as:
A. Raw material inspection (includes chemical and physical mechanical characters inspection),
B. Machining process dimensional inspection (includes: 1st pc inspection, self inspection, final inspection),
C. Heat treatment result inspection,
D. Gear tooth inspection (to know the achieved gear quality level),
E. Magnetic particle inspection (to know if there’s any cracks in the gear).
We will provide you the reports 1 set for each batch/ shipment.
| Application: | Wind Turbine |
|---|---|
| Hardness: | Hardened Tooth Surface |
| Gear Position: | External Gear |
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|
.shipping-cost-tm .tm-status-off{background: none;padding:0;color: #1470cc}
|
Shipping Cost:
Estimated freight per unit. |
about shipping cost and estimated delivery time. |
|---|
| Payment Method: |
|
|---|---|
|
Initial Payment Full Payment |
| Currency: | US$ |
|---|
| Return&refunds: | You can apply for a refund up to 30 days after receipt of the products. |
|---|
What are the safety considerations when working with sun gears in machinery?
Working with sun gears in machinery requires careful attention to safety to prevent accidents and ensure the well-being of operators. Here are some important safety considerations when working with sun gears:
- Training and Knowledge:
Operators and maintenance personnel should receive proper training and have a thorough understanding of the machinery’s operation and the specific risks associated with working with sun gears. This includes knowledge of safety procedures, maintenance protocols, and the use of personal protective equipment (PPE).
- Lockout/Tagout Procedures:
Before performing any maintenance or repair tasks on machinery involving sun gears, it is essential to follow lockout/tagout procedures. These procedures involve isolating the machinery from its power source and ensuring that it cannot be accidentally energized during maintenance. Lockout/tagout procedures help prevent unexpected movements of the gears, reducing the risk of injury.
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE):
Appropriate personal protective equipment should be worn when working with sun gears. This may include safety glasses, gloves, protective clothing, and hearing protection, depending on the specific hazards present. PPE helps protect operators from potential injuries caused by flying debris, contact with moving parts, and excessive noise.
- Machine Guards:
Machine guards should be in place to prevent accidental contact with the sun gears during operation. Guards can be physical barriers, such as covers or enclosures, that restrict access to the gears. They act as a protective barrier and reduce the risk of entanglement or injury caused by accidental contact with rotating or moving parts.
- Maintenance and Inspection:
Regular maintenance and inspection of machinery, including sun gears, are crucial for identifying potential issues and preventing malfunctions or failures. Maintenance tasks should be carried out following manufacturer guidelines and recommendations. Inspection of gears should include checking for signs of wear, proper lubrication, and alignment.
- Proper Handling and Lifting:
When handling sun gears or transporting them within a facility, proper lifting techniques and equipment should be used. Sun gears can be heavy and require appropriate lifting devices, such as cranes or hoists, to avoid strain or injuries. Operators should also ensure that gears are securely fastened or stored to prevent them from falling or causing accidents.
- Risk Assessment:
A comprehensive risk assessment should be conducted to identify hazards associated with sun gears and their machinery. The assessment should consider factors such as gear size, rotational speed, pinch points, and potential for entanglement. Based on the assessment, appropriate safety measures and controls should be implemented to mitigate identified risks.
- Emergency Procedures:
Clear emergency procedures should be established and communicated to all personnel working with sun gears. These procedures should include protocols for responding to accidents, injuries, or equipment malfunctions. Operators should be familiar with emergency shutdown procedures and know how to safely stop the machinery in case of an emergency.
By adhering to these safety considerations, operators and maintenance personnel can minimize the risk of accidents and promote a safe working environment when working with sun gears in machinery.
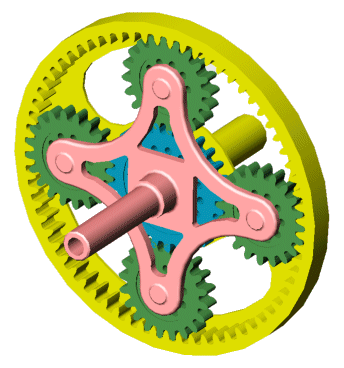
Can sun gears be used in high-torque applications?
Sun gears can indeed be used in high-torque applications and are commonly employed in various mechanical systems that require substantial torque transmission. The design and characteristics of sun gears make them capable of handling significant torque loads. Here’s an explanation of why sun gears can be used in high-torque applications:
- Central Positioning: Sun gears are typically located at the center of planetary gear arrangements. This central positioning allows them to distribute torque to multiple planet gears, which then transfer the torque to the outer ring gear. The central position of the sun gear enables efficient torque transmission and load sharing among the gears, making it suitable for handling high-torque applications.
- Torque Amplification: The arrangement of sun gears in a planetary gear system allows for torque amplification. By utilizing the interaction between the sun gear, planet gears, and ring gear, the gear system can multiply or reduce torque based on the gear ratio configuration. In high-torque applications, this torque amplification capability of sun gears is advantageous as it allows for the multiplication of input torque, resulting in higher torque output.
- Sturdy Construction: Sun gears are designed to withstand high torque forces. They are usually made from durable materials such as hardened steel or other alloys with high tensile strength. This robust construction ensures that sun gears can effectively handle the transmitted torque without experiencing excessive wear or deformation.
- Load Distribution: The interaction between the sun gear, planet gears, and ring gear in a planetary gear system enables effective load distribution. By distributing the torque across multiple planet gears, the load is shared, reducing the stress on individual gears. This load distribution mechanism enhances the overall durability and torque-handling capacity of the gear system, making it suitable for high-torque applications.
- Customizable Gear Ratios: Sun gears in planetary systems allow for the customization of gear ratios. By changing the number of teeth on the sun gear, planet gears, and ring gear, as well as their relative sizes, the gear ratio can be tailored to meet specific application requirements. This flexibility in gear ratio control enables the optimization of torque output for high-torque applications.
In summary, sun gears can be effectively used in high-torque applications due to their central positioning, torque amplification capability, sturdy construction, load distribution mechanism, and customizable gear ratios. These characteristics make sun gears reliable and suitable for transmitting substantial torque in various mechanical systems.
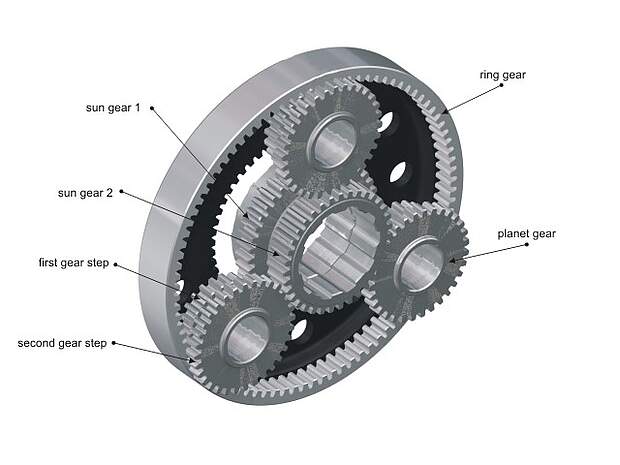
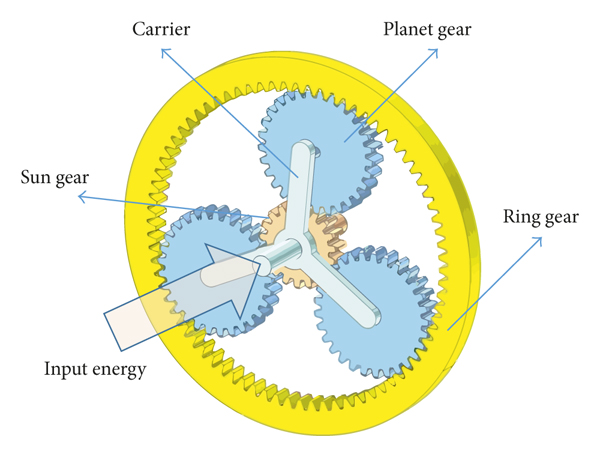
What is a sun gear and how does it function in gear systems?
A sun gear is a fundamental component in gear systems, particularly in planetary gear arrangements. It plays a crucial role in determining the overall gear ratio and power distribution within the system. Here’s an explanation of what a sun gear is and how it functions:
A sun gear is a central gear in a planetary gear set. It is typically located at the center of the gear arrangement and is surrounded by other gears, known as planet gears, as well as an outer ring gear, also called a ring gear or annulus.
The primary function of the sun gear is to transfer torque and provide the driving force in a planetary gear system. Here’s how it functions:
- Power Input: The sun gear receives power input from an external source, such as an engine or motor. It is directly connected to the input shaft and receives rotational motion and torque.
- Planet Gear Engagement: The sun gear engages with multiple planet gears, which are smaller gears that surround the sun gear and mesh with both the sun gear and the ring gear. The planet gears rotate around their own axes while also revolving around the sun gear.
- Power Distribution: As the sun gear rotates, it transmits torque to the planet gears through their meshing teeth. The planet gears, in turn, transfer the torque to the ring gear. The relative sizes of the sun gear, planet gears, and ring gear determine the gear ratio and the distribution of power within the system.
- Gear Ratio Variation: By changing the arrangement and sizes of the sun gear, planet gears, and ring gear, gear systems can achieve different gear ratios. The number of teeth on the sun gear, planet gears, and ring gear, as well as their relative sizes, determine the gear ratio. This allows gear systems to provide various output speeds and torque levels, catering to different operational requirements.
- Directional Control: In some gear systems, the sun gear can also serve as a means of controlling the direction of power transmission. By fixing or holding the sun gear while the ring gear or planet carrier is driven, the gear system can achieve different output directions, such as forward or reverse rotation.
In summary, the sun gear is a central gear in planetary gear systems, responsible for receiving power input, engaging with planet gears, distributing torque to the ring gear, and determining the overall gear ratio. Its function is crucial in achieving different speed and torque combinations, as well as controlling the direction of power transmission within gear systems.


editor by CX 2023-11-03